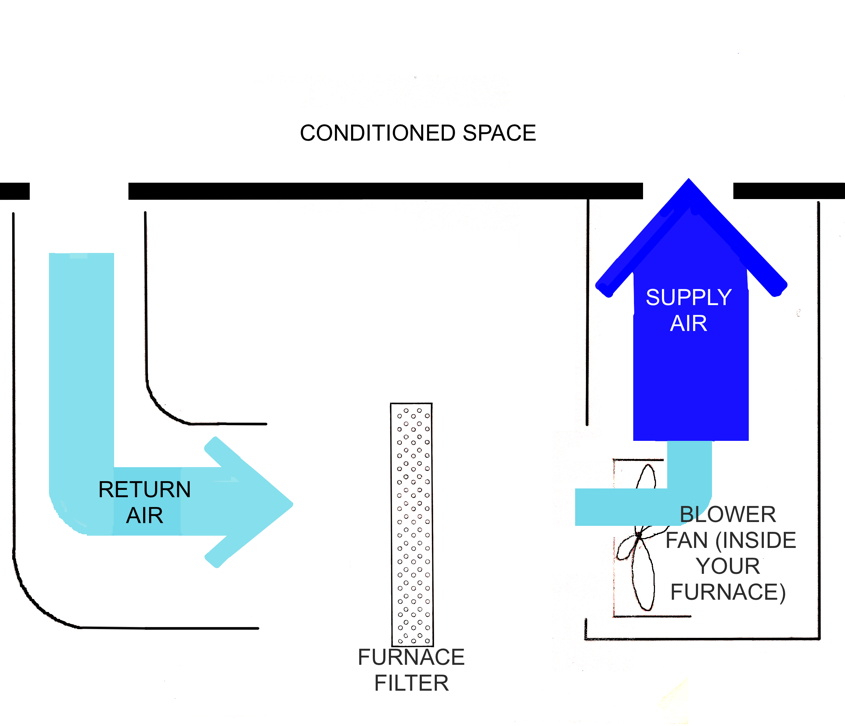
Furnace filters: filtering vs. airflow
When my new furnace was installed, I was pretty much convinced that washable filters were the way to go in comparison with filters that you throw away. It should be a no brainer, you don’t throw away washable products contributing to the landfill, and it should save you money by not having to pay for disposable filters. After some closer inspection and some research, washable filters work great in theory, but might not actually be the best choice for a furnace filter for every HVAC system for a number of different reasons. If your airflow is not very restrictive, you wont filter much (really cheap fibreglass $1 filters), but if you filter to much, then you will have no airflow, and poor system performance. The key to understanding this principle is knowing that there must be a balance between filtering and airflow. Before a choice is made, it is important to understand how filters impact your system and where the balance lies.
The more airflow you have, the better your system will run
Lets pretend for a moment, that you want to filter out as many particles as possible, so you decide to use a filter with dense material usually having a higher MERV rating. This obviously a great way to filter as many particles as possible, but it comes at a high price. Literally. You see, the filter itself is an obstruction in your HVAC system. It is literally placed in the centre of the duct, a duct that has flowing air. In the above example the air could be passing through the duct at 2 meters per second (before it hits the filter). After the air passes through the filter, the airspeed is slightly decreased. It could now be 1.9 meters per second or even more. The light blue arrows shows the reduction in volume of air that passes through the duct every second. After the air passes through the filter, the blower fan in the furnace engages and moves more air (dark blue) to compensate for any loss in volume passing through the system when heat is required. The lower the airflow, the longer that motor has to work.
Other factors that play a role in how hard the blower works include the condition of your ducts including undersized ducts, poor fittings length of ducting. It is very common to have a return duct that was knocked loose during a renovation, that is now inside your wall. Air-conditioning requires larger diameter ducting than your heating system requires. Therefore your duct size should be dictated by air-conditioning needs. This means that many people may have ducts that are too small if their house was constructed before air-conditioning became widespread in the 1950s and 1960s. Very often, in older homes, return ducts were not installed at all. All of these factors play a role in the air pressure difference between the supply and the return air ducts.
If this is at all confusing, that’s fine, you can hire an HVAC technician to figure out if you have an issue with your ducts. Ask them to perform a test called a “static pressure drop” to determine the amount of resistance in your system between the supply and return. By knowing the resistance you currently have in the system, how know how much resistance you can afford (using a more restrictive filter). This static pressure value attained from this test is used in a chart that is usually located in the instruction manual of your particular furnace, and that chart dictates what your pressure losses are. This is not a DIY test or even for a handyman. Special equipment is required to perform it unless you happen to be an expert in fluid dynamics. If your HVAC technician does not know how to perform this test, find a new HVAC company. This stuff is literally HVAC 101, and you would be surprised at some of the hacks out there. Side note, never have your furnace installed from a company that does not service equipment as well. You will save yourself a load of trouble in the future. Trust me.
Your restrictive filters can cause higher utility bills and increase your carbon consumption, and ruin your furnace components.
If your filter is more restrictive, it can have a huge impact on your energy consumption, and will hurt your over HVAC system efficiency. Your system will react to your restrictive filter. In heating mode, your system will turn on more often, burning more fuel than if it was less restricted and your 95% variable speed ECM motor is now running at full speed. Not only are you burning up more energy now, but if your components are running at full speed all of the time, when they were designed to run at full speed some of the time. This increased duty-cycle, reduces the life of your your motor. It is not uncommon for these components to fail in less than 10 years in these type of conditions. Some motors are designed to run longer, but most dont. It is also common practice for alot of companies to replace the whole motor rather than just one component. Expect to pay $1500 to $2000 for that repair.
Why is that room so hot in the summer? (or cold in the winter)
If some of your rooms in your house always too hot, (or too cold in the winter), using a restrictive filter will impede the volume of air to reaching those spaces at all in the amount you need. This is especially the case in the summer due to the higher requirements for airflow. Try swapping your filter to one with good airflow to see if it makes a difference in comfort level. You will have to wait a day or two before you will notice a difference. This alone can make a difference in temperature and airflow for some spaces.